Our lives are made up of simple activities that help us thrive, be social, maintain…

NEURO RTMS
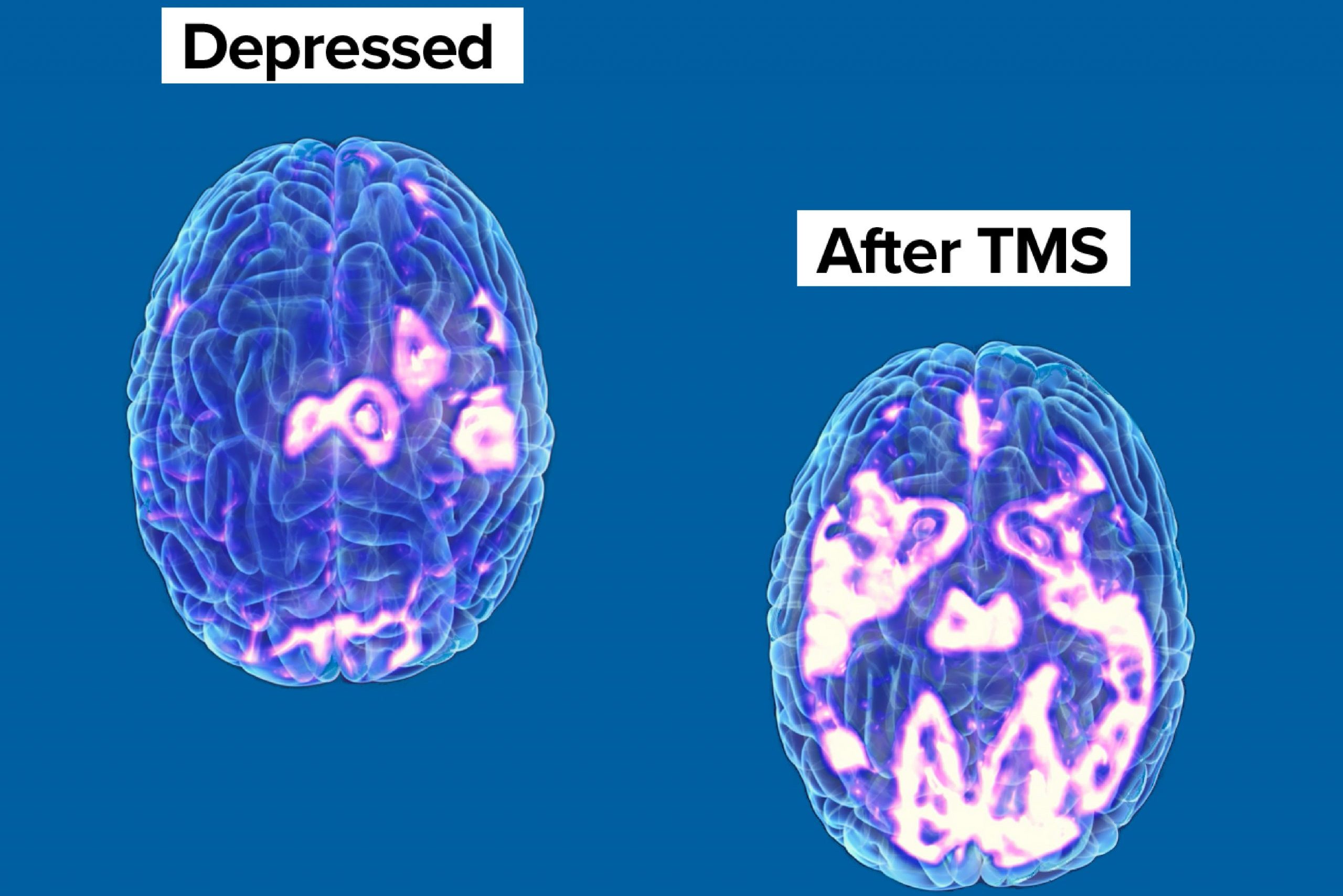
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, also known as TMS, has emerged in past decades as an impactful non-invasive alternative to traditional treatment for a host of neurological issues and disorders. A procedure in which a pulsed magnetic field triggers the cerebral hemispheres, TMS uses magnetic stimulation to bypass various current pulses on the specified part of the brain. The pulses are produced by a coil encased in plastic held closely to the scalp. TMS has established itself as an effective alternative to chronic, medical-resistant depression.
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, also known as rTMS, is a modification of traditional TMS with the capability of penetrating through the scalp and skull safely, without any form of pain. This mechanism is termed repetitive due to the fact that the magnetic stimulation is delivered in regular intervals.
It is also important to note that most rTMS stimulation can be changed anytime, depending on the condition of each individual’s neurological issues. The ability to change these parameters while marking specific brain regions has been shown to have a significant beneficial therapeutic impact on the treatment of depression. I will write in more detail more about the customization of TMS in a future blog
Methods of rTMS Application
This therapeutic treatment model can be applied as a single pulse or in pairs. However, when applying in pairs, the pulses are separated with strategically placed pauses, called interstimulus intervals (ISL). ISL can be applied to the same or different areas within the brain. Depending on the target location within the brain, stimulation can be used to excite the target site or suppress excitability in the target site.
The application of the magnetic pulse in this fashion is meant to activate the contralateral muscles of the body. The results of this application can be recorded through electrophysiology categorized under motor-evoked potentials.
Established Applications of Neuro rTMS
Presurgical Language Mapping
TMS has been shown to induce speech arrest, which is crucial to support the recovery of neurosurgical patients who experienced left hemispheric lesions through an object naming exercise. The results showed that there is a strong correlation between presurgical language mapping with TMS.
Presurgical Motor Mapping
rTMS also has the capability of targeting specific brain regions to better understand motor responses induced by each of these sites. This specificity makes it easy to assess the areas of the cortex that can be exercised safely during tumor resection. Data gain can also be applied during the removal of an epileptogenic focus without taking much attention on postoperative motor deficits. rTMSperform the functions above with high levels of accuracy similar to invasive cortical mapping mechanisms.
Treatment of Major depression
TMS is especially effective when it comes to the treatment of major forms of depression that do not respond to medications. The magnetic stimulation generated by TMS therapy on a daily session triggers specific parts of the brain related to depression. TMS utilizes a unique mechanism that plays an essential role in the management and treatment of depression.
Therapeutic Applications of rTMS in Neurology
Even though TMS has not yet been proved to be a treatment modality for neurologic diseases by the FDA, it showcases excellent success in this treatment area. Currently, TMS is applied in a diverse range of neurologic conditions. TMS shows substantial promise in the management of numerous medical disorders, including but not limited to:
Movement Disorders
rTMS can manage primary motor cortices and improve bradykinesia disease. To address the condition, low-efficiency levels of rTMS have been applied on cortical excitability and on different premotor regions. It is evident that movement-related complications are mainly caused by the neurology system. rTMS plays a significant role in repairing the neurology system supporting the entire movement system.
Tinnitus
The application of rTMSon the primary auditory cortex has significant success in reducing Tinnitus. According to most studies, low frequency is mainly used, though the optimal parameters are not yet clear.
In addition, the continuous application of rTMS showcases a higher degree of interindividual variability in different aspects such as loss of hearing, variability in age, and chronicity level of the condition.
Stroke Rehabilitation
Stroke is among the medical disorders that have become rampant in the current world. For this, TMS is employed to take part in the suppression of the contralesional cortex or to augment cortical excitability that causes the condition.
Individuals that suffer from stroke always require motor recovery that is relevant during the healing process. Studies have revealed that applying TMS paradigms in the improvement of aphasia and hemispatial neglect caused by stroke may have significant benefits.
Chronic Pain
Initially, it was believed that chronic pain is mainly associated with old age. This is not the situation since it has become a significant health hazard among young and aged individuals. TMS has shown remarkable results in improving chronic pain among patients with neuropathic pain. This pain is mainly associated with the peripheral nerve, central sensory pathway, and spinal cord.
TMS therapy stimulates various parts of the body associated with chronic pain, thus helping in the management of the condition. However, TMS works well on relieving chronic pain when you carry out the therapy sessions repeatedly. Note that this model responds well when compared to the medical route of treatment.
Conclusion
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation plays a major role in managing and treating a wide variety of conditions. However, the effectiveness of the therapy depends on a variety of factors that the specialist primarily considers for the well-being of the patient.