Our lives are made up of simple activities that help us thrive, be social, maintain…
TRANSCRANIAL MAGNETIC STIMULATION (TMS) THERAPY: ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW
Over the years, various kinds of stimulation therapy have been explored to treat neurological (brain-related) and behavioural issues that have not responded well to traditional medications or treatment. Uses alongside or even to replace the most common prescription medicines, stimulation therapy treats muscle spasms, chronic pain, and a variety of neurological illnesses.
Generally, stimulation therapy encourages or causes noninvasive development or change in neuronal activities of nerve cells. The idea is that the simulation procedure is to provoke the nerve cells into actions that initiate recovery from illnesses. For such therapies, both electric and magnetic forces have been applied with an impressive degree of success.
One of the most common examples of stimulation therapy is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) which gained public attention as an effective treatment for patients suffering from depression. Since that time, TMS has been shown to be a viable and effective treatment for a wide range of brain and behaviour issues.
What is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is an alternative brain stimulation therapy that employs electromagnetic pulses to treat neurological disorders like depression. TMS targets the nerve cells with electromagnetic pulses, causing effects that stimulate improvement of patients’ mental health.
It is no longer unusual to find patients who do not respond to medications for certain neuronal illnesses. In such instances, the need for stimulation therapy becomes almost inevitable. For example, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy has become quite popular, particularly in treating depression. It became a necessary alternative to help patients who do not respond to antidepressant prescriptions and those whose cases make psychotherapists doubt their license.
Interestingly, TMS has shown tremendous results in improving symptoms of neurological or mental health disorders through the use of electromagnetic pulses. These electrical impulses are designed to be repetitive, which also determines how the TMS treatment procedure works. As a result, TMS is also called repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS). Unsurprisingly, professionals use both terms interchangeably.
In addition to the treatment of depression, TMS has shown incredible evidence that the electromagnetic pulses could improve anxiety, Parkinson’s treatment and a host of other disorders.
Stimulation therapy technology, like many groundbreaking innovations, are particularly prized for their procedural simplicity. The case is not different for TMS, which employs a simple and convenient procedure for both doctor and patient handling mental health problems.
In this article, we cover the exciting questions:
- How does Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) work?
- What are the benefits of TMS?
- What are the side effects of TMS?
- When should patients avoid TMS treatment?
- When should TMS be recommended as an alternative treatment for neurological disorders?
- What does it cost to get TMS therapy?
- At what rate has TMS proved successful in neurological treatments?
How does Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) work?
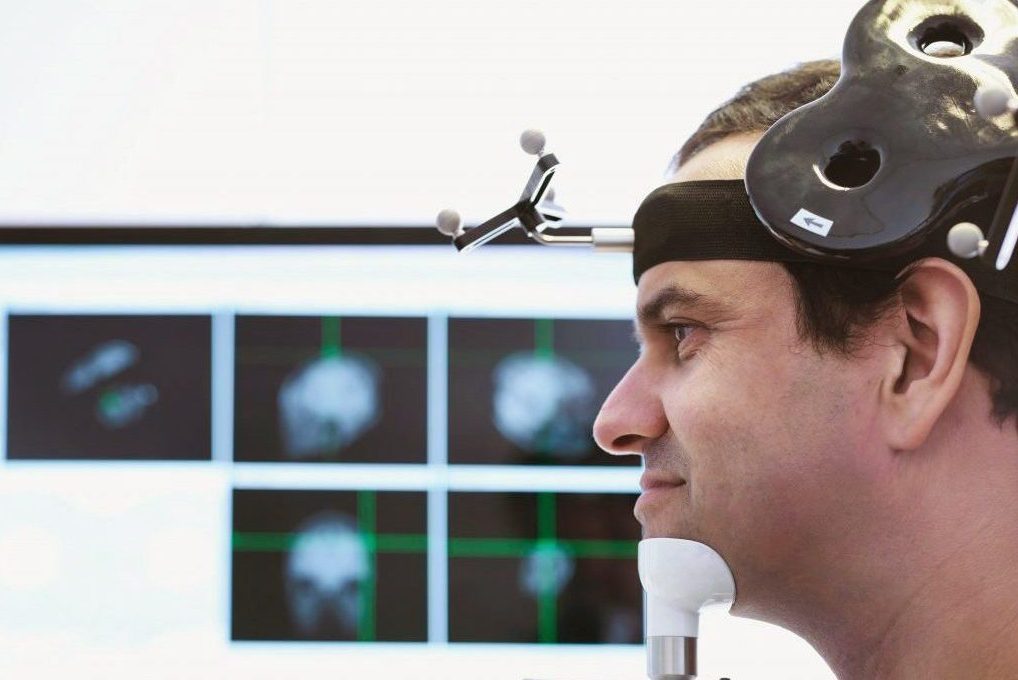
The application of the TMS treatment involves a simple process. The first step consists in placing the electromagnetic coil around the patient’s cranium, particularly near the forehead. After this arrangement, the coil delivers magnetic pulses targeted to provoke or stimulate the nerve cells that control mood.
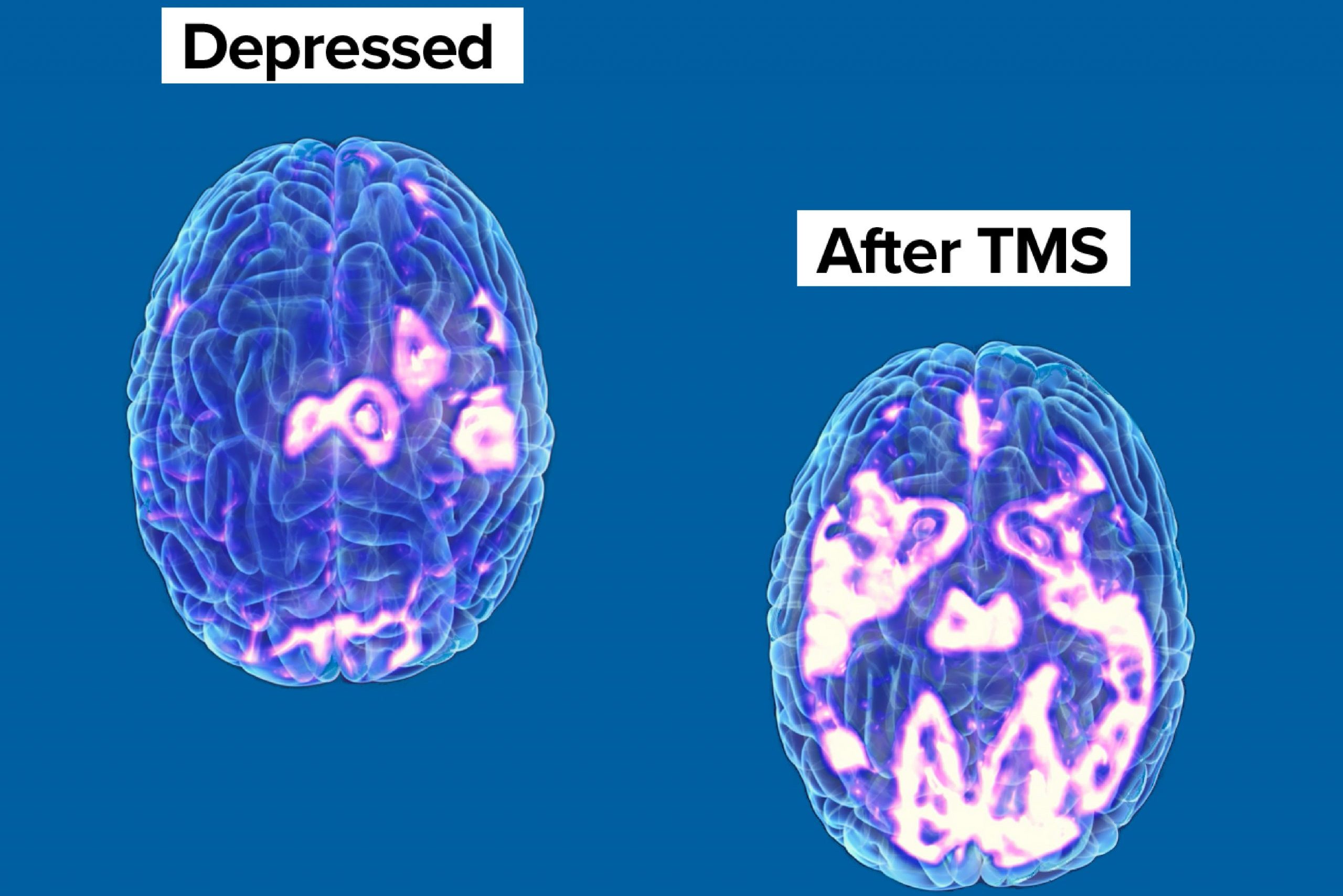
This mood control is precisely where the use of TMS for depression treatment comes into play. According to this research, the leading cause of depression is reduced activities in the brain’s prefrontal cortex. When the pulses stimulate the nerve cells, they trigger the activity level in this part of the brain where depression has slowed down actions.
TMS influences or alters the pattern of the brain’s activities. More specifically, changing the brain’s actions is particularly essential for patients whose depression has been unresponsive to traditional antidepressants or therapeutic approaches.
The use of TMS in the treatment of neurological illnesses continues to expand. The technology is progressing, and experts will gradually perfect the therapy in adaptable ways to treat other disorders with increasing efficacy.
What are the benefits of TMS?
Aside from the initial treatment of depression, TMS has shown strong results in treating a variety of other disorders. These include:
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Generalized Anxiety Disorders (GAD)
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Stroke Rehabilitation
- Parkinson’s
According to this study, TMS could induce the release of dopamine for Parkinson’s treatment. The study claims that a dysfunction of dopamine plays a significant role in causing Parkinson’s among other diseases.
This study shows that transcranial magnetic stimulation could lead the prefrontal cortex to release dopamine in the ipsilateral caudate nucleus. This release of dopamine in the midbrain triggers a chain of events that could improve the health of patients suffering from Parkinson’s.
- Schizophrenia
TMS has been proposed by many professionals as a therapy for schizophrenia treatment. This proposition stemmed from the fact that many sufferers of the mental health conditions do not respond to antipsychotic medications. Particularly for patients who experience frequent auditory hallucinations, this research shows that transcranial magnetic stimulation holds some promise to supplement conventional medications.
- Alzheimer’s
For now, Alzheimer’s treatment with transcranial magnetic stimulation has not proven to possess long-term efficacy. However, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is one of the multiple neurocognitive disorders which noninvasive brain stimulation therapy could improve.
Regardless of the knowledge gap which still exists as to the full potential of the use of TMS for Alzheimer’s therapy, rTMS promises desirable influence on AD pathogenesis.
- Nicotine Addiction
Much like the case of Parkinson’s, research has shown that a dysfunction in dopamine could worsen cases of drug addiction. Smokers with this dysfunction may struggle to quit smoking for example. At the moment, TMS technology is not fully developed to help patients struggling with nicotine addiction. However, the noninvasive brain stimulation therapy could induce the release of dopamine to the midbrain. Particularly for patients who need help to quit smoking, the inducement of dopamine release could trigger their improvement.
- Sclerosis
Given the fantastic evidence which stacks a pile of promises on possible use of rTMS in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders, it is not strange that it has been considered for the treatment of multiple
What are the side effects of TMS?
Although research into TMS continues, the most common side effects that have been confirmed include:
- Mild headaches
- Pain in the scalp
- Lightheadedness
- Twitching of the face
- Sleepiness
- Tingling
- Neck pain
- Seizures (rarely occurs)
When should patients avoid TMS therapy?
- TMS therapy does not pose safety challenges except for patients who have some form of metals in their bodies, including:.Metal plates
- Bullet pieces
- Electrodes
- Metallic ink tattoos on the face
- Stents for brain or neck
- Piercings
- A cochlear implant, etc.
When should TMS be recommended as an alternative treatment for neurological disorders?
As research progresses, TMS is currently only recommended for treating patients for whom traditional medications and therapeutic approaches are not effective.
Doctors may even recommend that the patient tries a different antidepressant before resorting to TMS. Also, TMS is more easily recommended for younger patients because they experience the adverse effects of antidepressants more.
What does it cost to get TMS treatment?
A course of TMS therapy costs an average of $9,000. While the patient’s health insurance might provide some coverage, most insurers stipulate that the patient has tried as many as four different antidepressants before considering TMS.
At what rate has TMS proved successful in neurological treatments?
TMS is still used primarily to treat depression and has been shown to have a success rate of between 30% and 64%.
For now, the success rates of the therapy in treating other neurological illnesses are yet to be ascertained.
Conclusion
The use of TMS therapy in treating neurological disorders aims to influence the activities of the affected part of the brain. This interruption of the regular pattern of the brain improves the mood and condition of patients suffering from depression and other neurological and behavioural issues.
While TMS seems to have shown extraordinary efficacy in depression treatment and other mental health conditions, it remains the last recommendation a doctor would offer. The reason is that the technology is not fully developed, and neither are the possible side effects fully known.
Also, aside from depression treatment, TMS has shown signs of efficacy in PTSD treatment and other neurological disorders, and TMS is also used as an erectile dysfunction therapy.
Please, feel free to contact us for inquiries and more information regarding TMS therapy.
Contact Us Now!